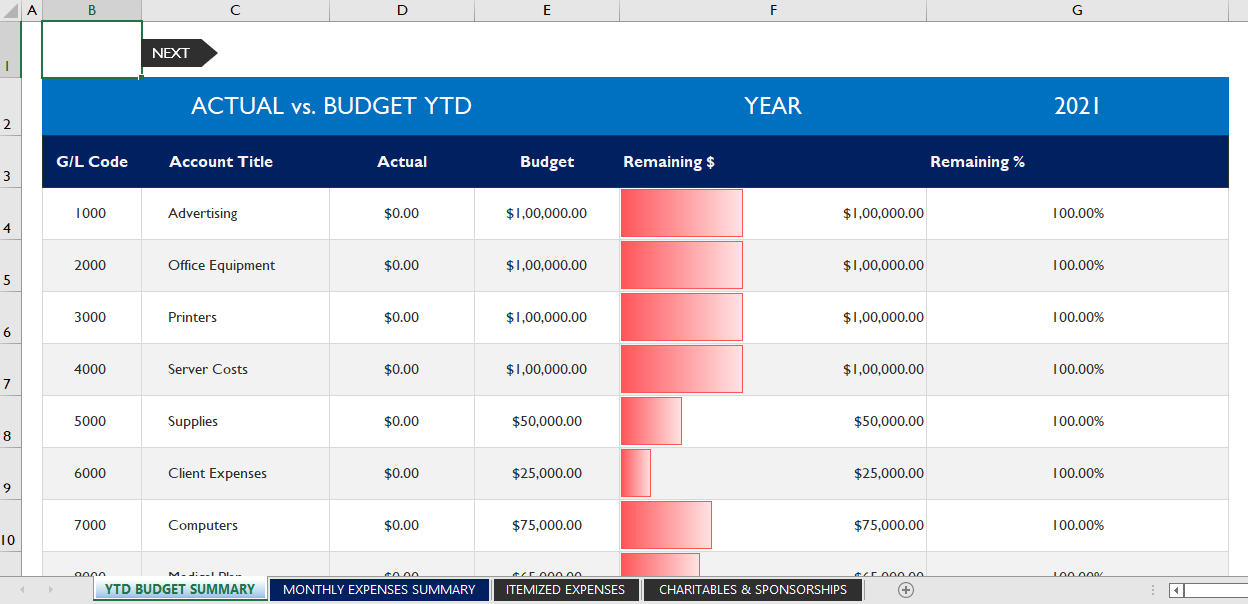
Budget Variance Analysis Excel Template consist of various worksheet for computing budget variance analysis, expenses variance analysis, and general ledger wise variance analysis. We have defined formula in every field for automatic calculation for variance analysis. Furthermore, it has conditional formatting, so that you can visually analyze the data. However, Before you download this Excel template, You must refresh you understanding about why do we need variance analysis.
What Is a Budget Variance?
Every business owner should have a budget which lays out the company’s future course of action. A budget helps to showcase from where the sales would come. Moreover, It gives overview of source of funds that would be spent to meet the target sales.
While budgeting variance could be a great planning tool, it’s also a useful management tool for keeping the business on a right track to meeting its objectives. For accomplishing business goal, budgeting and variance analysis provides key insights and foresight to assist the management in taking prompt and feasible decisions.
Importance of a Budget Variance
A variance can either be “favorable” or “unfavorable”. A positive variance means actual revenue is higher than budgeted revenue, or expenses are lower than estimated. The result could be higher income than originally forecast. Conversely, an unfavorable variance means forecasted revenue is not met or Incurring excess expenses than estimated. As a result of the variance, net income may lower than estimate.
In case of material variances , management should review in details and perform root cause analysis. Then, accordingly management will identify remedial action plan. The definition of material is subjective and different depending on the company. Relative size of the variance. However, if a material variance persists over an period of time, management likely needs to evaluate its budgeting process.
Key Takeaways
- As per accounting terms, a budget variance analysis is what where actual costs are either higher or lower than the standard or projected costs.
- An unfavorable, or negative, budget variance is indicative of a budget shortfall, which may occur because revenues miss or costs come in higher than anticipated.
- Variances may occur for internal or external reasons and include human error, poor expectations, and changing business or economic conditions.
How to Compare Budget vs Actual Through XLSX templates?
A small business budget is of no use if you do not compare it against actual performance. This important method of evaluating business performance stands as one of the most important monthly financial reports for any company. If you perform any forecasting or budgeting, learn the best practices for budget vs actual analysis.
What is Budget vs Actual Variance Analysis?
A Budget vs Actual Variance Analysis allows you to evaluate business performance against your plan, analyze the cause of financial deviations, and inform appropriate management decisions. Some bookkeeping services include a budget variance analysis report, but many small business owners will need to build their own.
If you do not have a business budget, you may choose to instead compare projected or forecast results against actual results. This has the added benefit of validating the accuracy of your forecast and improving financial planning.
Small business owners often think budget variance analysis is meant solely for income and expenses. In reality, best practice is to perform variance analysis balance sheet and statement of cash flows too.
Why is it a good idea to compare budget against actual figures?
Budgeting is a critical planning process, but you will never “stick to your budget.” That’s ok – the point of a budget is to set expectations you can measure performance against. Comparing actual results against budget allows you to measure your year-to-date performance, judge whether the company is trending ahead or behind plan and adjust management tactics accordingly. Without reports to measure your performance, you are flying blind.
How do you analyze budget vs actual?
Follow these 6 steps to build a simple variance report:

- Create a new spreadsheet separate from your financial forecasts.
- Your summarized or detailed income and expense accounts in the first column.
- Enter your budgeted values for each profit and loss account for January in the second column.
- Enter the actual values for each P&L account for January in the third column.
- Create a “variance” formula in the fourth column (actual minus budget.)
- Create a “variance %” formula in the fifth column (variance / budget)
Repeat this process for every month for the P&L, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and KPIs. Accounting services like CFOshare will use integration, ETL, or other advanced techniques to automate this process; but, unless you are experienced at these advanced techniques, we recommend a simple manual entry process.
Review the variance column every month. Take time to understand:
- Large variances. These are key drivers to your company’s performance.
- Consistent, reoccurring variances. This indicates budgeting or forecasting error; or lack of discipline in business management (especially for unfavorable expenses.)
- Variances growing each month. This is an early warning of a growing trend management should be aware of.
When reviewing each budget vs actual variance, ask yourself these questions:
- Is this variance good or bad for the company?
- What actions or lack of actions resulted in this performance?
- What actions should management take given this result?
- Should management stick with this strategy, invest more in this strategy, or pivot to change strategies?