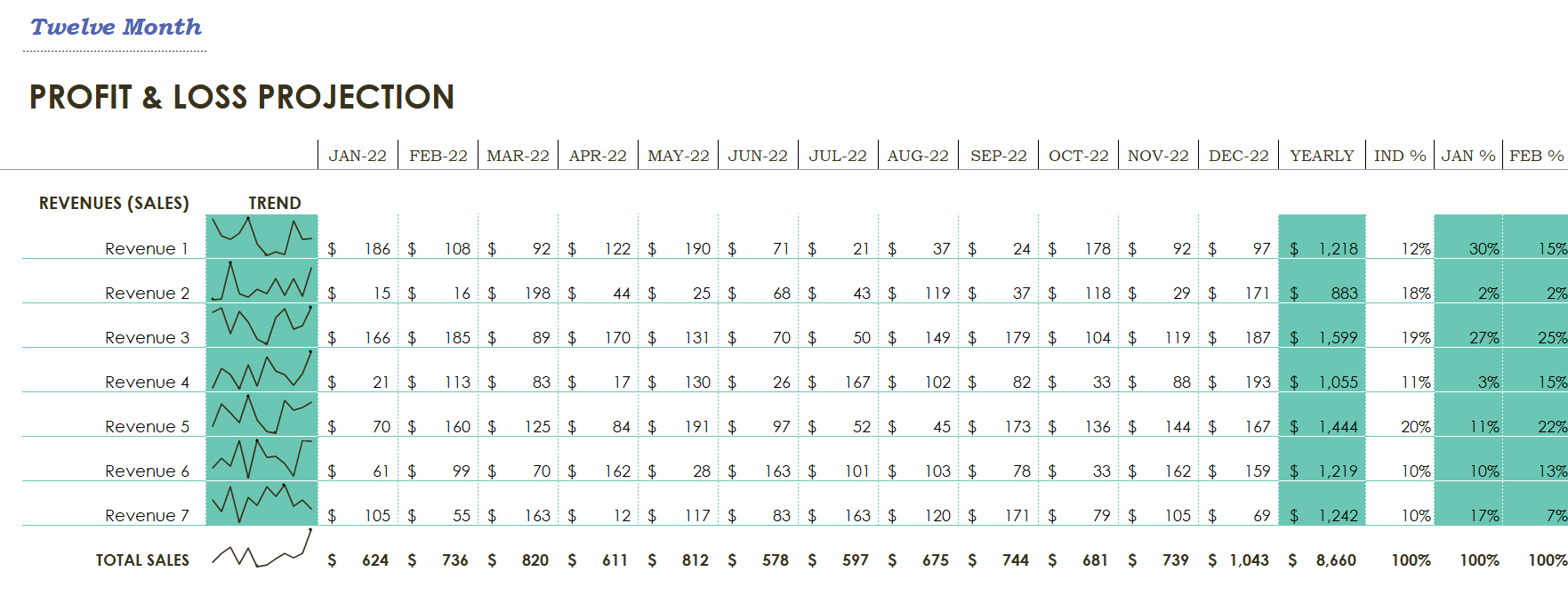The short term prediction is not a necessary part of a basic business plan. So, the yearly Profit and Loss Statement is an excellent tool to help your thinking about the organization’s future. Furthermore, capitalists will almost want growth prospects. Use this Long Term Prediction for Company’s Profit. The record contains the business details for 1 week, 3 months, 6 months, or even 1-2 year income and expense. The essential part of long term planning is not the figures themselves, but the fact underlying the numbers. So make sure your facts are clear and in detail in a narrative attachment. This will communicate your vision of the company’s future.
This spreadsheet is a twelve-month P & L. That helps you do some planning about funding growth
The categories for Funding Growth
Income Tax:- This allows you to estimate how much your Profit is and information about Funds.
Net Profit:- Net Profit for a Twelve-Month Profit
After-Tax:- Funds Left for company’s to use
Earning:- Profit that left in the company to increase Equity and Fund Growth
How to use Profit and Loss Statement in Excel
Just simply add Enter Data on sales, income, taxes and expenses in the template.
If you also like to perform a cash flow analysis and are searching for a 12-month profit and loss worksheet, So all you need to do is change the title to “12-Month or Yearly Profit and Loss Statement. Use this profit and loss template below for a monthly cash flow analysis by changing the column from years to months.
The Profit and Loss Statement Spreadsheet helps you create a 4-year projection of income and expenses for your trade. It uses the same list of categories as the business budget, but also contains columns for calculating the Percentage of Total Sales, which helps you to analyze the cost of sold and operating expenses.
This sheet contains two profit and loss templates that are planned for organizations providing services or selling.
The worksheet includes a Cost of Stuff Sold section for recording purchase and calculating Gross Profit.
The main Category of Profit/Loss Statements are
- Net Income
- Revenue
- Taxes
- Costs of Sales
- Selling, Administrative and General Expenses
- Marketing and Advertising
- Interest Expenses
Importance of Profit and Loss Projection
To calculate Net Profit
Your net profit is the essential figure you need to determine. The Net Profit is money left after paying your overhead costs. An organization’s Net Profit is Net Income, Net Earning or Bottom Line. Represents the Financial Standing of an organization after all the Expenses paid from the total Revenues.
For Net profit, make a list of your monthly fixed costs categories;
Employee’s Salary
Insurance
Accounting, Tax Preparation and Advertising
Bookkeeping
To estimate the Gross Profit
The word gross Sales is reflect the sales made during a year. Services uses, the word Gross or Revenue, which reflect the value of benefits provided during the year.
So, it is known as gross revenue as per the bills raised for that time and less refundable taxes in fewer returns. Sales return, and sales allotment are deducted from this gross sale to arrive at the net sales number.
For example, subtract your average monthly varying costs from your measured average monthly sales revenue to get your monthly gross profit. This calculates how much of each dollar of sales you get to keep. That amount, however, you’ll have to pay for overall expenses; then left over is your net profit.
EXAMPLE: Subtracting costs of $5,500 per month from her sales estimate of $10,000 per month, Emme estimates her new average monthly gross profit will be $6,500
Gross profit margin
calculates the difference between the costs of producing a product or providing a service and what you’re selling. It lets you know how profitable your products and services are.
To calculate profit margin, divide your estimated average monthly gross profit by your approx monthly sales.
To estimate Net Income
Revenue is income earned by a person or a company from the sale of any products or services offered. Revenue known as sales is an income statement that shows how well a business performs.
Estimates how much you’ll take sales in each month during the next 6 to 12 months. Further, if you’re already in business, you can generalize from existing sales levels and allow for significant variables.
To Estimate Variable Costs
To estimate the monthly cost for the goods or services you’ll sell as part of achieving your sales estimate. This is a variable cost.
They’re called variable, or incremental because they go up or down depending on the products or services you produce or sell. In retail, they’re called “cost of goods”. For example, in an online-order business, then the more you sell, the more you’ll pay for shipping costs.
Other variable costs include supplies, materials, packaging, and sometimes labour costs used in providing your product or service.