How to create a profit and loss statement in excel
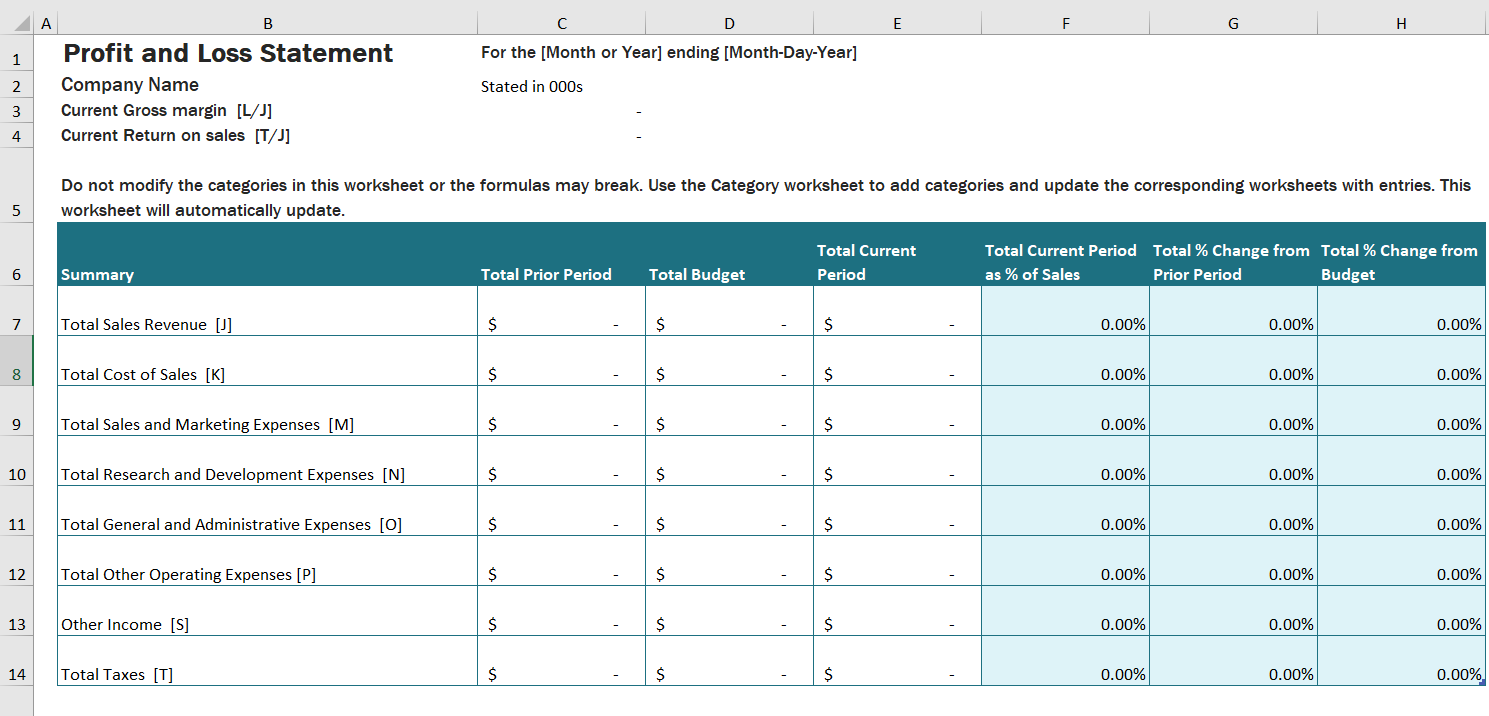
Don’t worry, you download free excel template down below this page. Profit and Loss Statement excel templates contains 5 different sheet of revenue, expenses and taxes etc. Further, Each spreadsheet have budget and actual column which helps you to compare profit and loss account for two different periods and budgets as well. It contains inter linking formulas which helps you to calculate your net profit very easily.
What is a profit and loss statement?
A profit and loss statement details a business’s income statement and expenses statement over a defined period. The P&L is also referred to as an income statement, statement of profit, statement of operations, and a profit and loss report. Regardless of the term used to describe this financial statement, it is a snapshot of a business’s revenue and expenses over a specific period. Typically, a P&L is made at least quarterly and annually, but they can be done more frequently.
The profit and loss statement is an economic statement that includes the income, costs, and expenses proficient during a business period. A financial statement in excel that provides a brief of a company’s expenses, income and profits or losses over a given period. Also, the P&L statement template shows a company’s capability to generate marketing, sales manage expenses and generate profits. The record contains the business details for 1 week, 3 months, 6 months, or even 1-2 year income and expense. This register will help the business owner and managers to know if they are going forward or backwards in business. It will importantly help the entrepreneur to know his/her business sustained profit and loss.
It also reveals money spent or cost obtained in a company’s effort to generate profit. The basic principles include income recognition, matching, and growth, which makes it different from the cash flow statement.
Key components of a profit and loss Account statement for small businesses
The P&L is comprises of two main parts: the income earned during the period of the statement and the expenses in the same period. These two parts are shown separately in the various entries relevant to your business. Not every P&L will have the same lines.
1. What is revenue and how to calculate revenue?
Revenue is first part on a profit and loss statement for small businesses and includes all income items. This entry on the P&L may be referred to as sales, gross receipts, fees, or any other term to describe the company’s operating revenue. Operating revenue is typically part out from non-operating sources of income, like interest.
Again, the accounting method affects when revenue is reported on the P&L. When using the accrual method of accounting, revenue is reported when earned, at the time of sale, even if payments have not yet been received. If you use the cash method , revenues is when you receive actual payments . To increase the accuracy of actual income, you need to adjust the gross sales may be based on past experience of customer returns or refund requests by setting up an allowance and netting it against revenues.
2. How to calculate Cost of goods sold (COGS)?
A company that sells goods must figure the cost of goods sold (COGS). This is essentially the cost of inventory or materials use to create products, which you need to subtract from the sales to determine the actual revenue (gross profit) from the sales. For example, a company that carries a $20 item in inventory and sells it for $100 would have $100 in revenue, but after taking the $20 of COGS into account would report $80 in gross profit.
3. Expenses
The expense portion of a profit and loss statement for small businesses encompasses any expenditure made to operate the business. These can include:
- Advertising costs
- Employee salaries, benefits, and payroll taxes
- Interest expenses
- Office supplies
- Payments to vendors or contractors
- Professional fees for accountants, attorneys, etc.
Accounting for some expenses requires understanding asset depreciation. Moreover, some purchases, such as office equipment, must be capitalize as an asset and written off over the useful life of the item. For example, Purchase of $1,000 computer, you cannot be write off the purchase for tax purposes, you need to capitalize and depreciate over five years. Each year the profit and loss statement reflects 20 percent of the cost for the computer, or $200 in expense.
Non-operating expenses, such as interest and taxes, are shown out separately from operating expenses for illustrative purposes.
4. What is gross profit?
Gross profit is the difference between the revenue or gross receipts and the cost of goods sold during the period. If the company is a service business without inventory, then the gross profit and the gross receipts are the same amount.
5. How to calculate Net profit or loss?
Post calculating any taxes due and subtracting them from pretax income, the net amount will equal a company’s net profit or loss for the period. When trying to compare companies in different industries and tax situations, or if exact numbers aren’t yet available. The net profit or loss is calculated to the earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA).